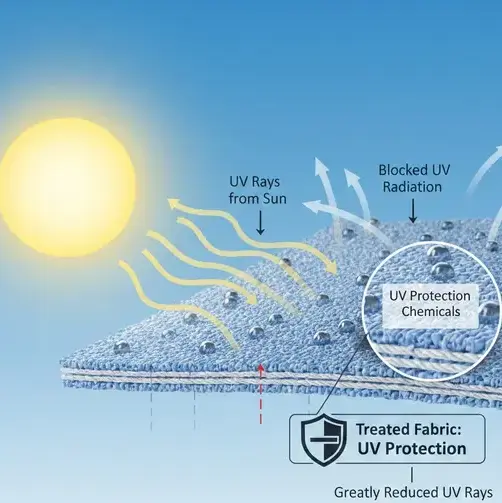
UV protection chemicals textiles are formulations designed to block or absorb ultraviolet radiation, preventing fabric degradation and skin exposure. By incorporating these agents, manufacturers improve the Ultraviolet Protection Factor (UPF) of fabrics and ensure compliance with safety norms such as OEKO-TEX and ASTM International. How do these chemicals ensure long-lasting fabric protection under harsh sunlight?
Key Takeaways
- By filtering ultraviolet rays, UV protection chemicals shield textiles and skin from radiation damage.
- Both organic and inorganic agents enhance UPF rating and color durability.
- Nano-finishing ensures long-lasting protection and wash stability.
- Eco-safe UV finishes comply with international safety and sustainability standards.
- Growing demand is observed in outdoor apparel, defense, and healthcare textiles.
What Are UV Protection Chemicals in Textiles and How Do They Work?
UV protection chemicals in textiles are finishing agents that reduce UV transmission through absorption, reflection, or scattering.
Mechanisms include:
- Absorbers: Convert UV energy into heat (e.g., benzotriazoles, benzophenones).
- Reflectors: Use UV-reflective particles like titanium dioxide and zinc oxide to minimize radiation penetration.
- Hybrid coatings: Combine the benefits of organic polymers and inorganic oxides for added durability..
These treatments are applied during dyeing, finishing, or coating processes to create UPF-rated textiles.
Which Chemicals Are Commonly Used for UV Protection in Textiles?
Typical UV-blocking compounds include both organic absorbers and inorganic pigments.
| Category | Examples | Function |
| Inorganic | Titanium dioxide (TiO₂), Zinc oxide (ZnO) | Reflect and scatter UV rays |
| Organic | Benzotriazoles, Benzophenones, Triazines | Absorb UV energy |
| Hybrid | Silica-TiO₂ composites | Enhance wash durability and optical clarity |
In India, textile processors often use Sarex Chemicals and Nicholas Fine Chem formulations for polyester, cotton, and blends.
How Are UV Protection Chemicals Applied to Fabrics?
Application methods depend on fabric type and intended performance:
- Exhaust Method: Immersion of fabric in UV chemical bath during dyeing.
- Padding Method: Application through mangle rollers ensuring uniform coating.
- Spray or Coating: For outdoor gear and technical textiles.
- Nano-finishing: Embedding nanoparticles for permanent UV resistance.
The treated fabric is then cured at specific temperatures to fix the chemical uniformly.
What Are the Benefits of Using UV Protection Chemicals in Textiles?
Key advantages include:
- Enhanced UPF Rating: Fabrics achieve UPF 30–50+ for maximum UV blockage.
- Color Retention: Prevents photo-fading and fiber oxidation.
- Skin Protection: Reduces UV-induced skin damage.
- Extended Fabric Life: Minimizes polymer chain degradation.
Outdoor wear, uniforms, and home furnishings benefit most from these protective coatings.
How Do UV Protection Chemicals Ensure Long-Term Fabric Performance?
Durability depends on chemical bonding and fiber affinity. Silane-based crosslinkers and nanoparticle dispersion improve adhesion and wash fastness. Post-treatment testing under ISO 105-B02 and AATCC 183 confirms long-term performance retention.
A textile chemical liquid frequently appears in conjunction with light stabilizers, finishing assistants, and coating agents designed for comprehensive UV protection.
What Role Do UV Protection Chemicals Play in Sustainable Manufacturing?
Modern formulations focus on eco-safe and non-toxic alternatives.
- Water-based dispersions reduce VOC emissions.
- Nano-mineral agents replace synthetic UV absorbers.
- Certified green finishes meet REACH and OEKO-TEX guidelines.
This aligns with the global move toward eco friendly chemicals in textiles, enhancing both product safety and sustainability.
What Are the Latest Innovations in UV Protection Chemical Technologies?
Recent advancements include:
- Smart Coatings: Photo-responsive agents that adjust UV absorption dynamically.
- Bio-based UV Absorbers: Derived from plant phenolics and lignin.
- Nano-encapsulation: Improves solubility and wash durability.
Innovative solutions like these are setting new standards for UV-protective fabrics across apparel and protective gear markets.

Conclusion
UV protection chemicals textiles combine advanced chemistry and surface engineering to safeguard fabrics and human skin from ultraviolet radiation. Continuous innovation and regulatory alignment are shaping the future of UV-protective fabric technology. For sustainable alternatives, manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco friendly chemicals in textiles to meet both performance and environmental goals.
FAQ
What chemicals are in UV protection?
Common chemicals include titanium dioxide, zinc oxide, benzotriazoles, and triazine derivatives.
How to make fabric UV protected?
Apply UV absorbers or reflective nanoparticles during the finishing process using pad-dry-cure or nano-coating methods.
What chemical protects from UV rays?
Titanium dioxide and benzotriazole compounds are most effective in blocking harmful UV radiation.
Are UV protection textiles washable?
Yes, high-quality UV finishes maintain 80–90% efficiency after 20+ wash cycles.
What fabrics naturally block UV rays?
Polyester, nylon, and tightly woven cotton have inherent UV resistance when enhanced with chemical finishes.
Sources
https://www.tib.eu/en/search/id/tema:TEMA20141001863/UV-Protective-Finishes-for-Textiles/#:~:text=Chemical%20finishes%20that%20provide%20protection,less%20permeable%20to%20UV%20rays.
https://www.hohenstein.in/en-in/expertise/health/uv-protection
http://www.nicholas.co.in/uv-protection-for-polyester-and-blends.html
https://www.redalyc.org/journal/429/42976206001/html/
https://www.fibre2fashion.com/industry-article/2328/uv-protection-finishes
https://www.sarex.com/textile/finishing-auxiliaries/uv-protective-agents
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9376596/
https://www.fuzhoutextile.com/news/uv-protection-fabrics-and-finishing-technologyupf50-textiles/





